- Home
- Technical Products
Enterprise Cloud IT Solutions
Industrial Measurement
- Solutions
Enterprise Cloud IT Solutions
Test Measurement
- Latest Articles
- About Us
 EN
EN
1G MRS - Managed Redundant Switch IP Core
Product Overview
The Managed Redundant Switch IP core (MRS) is a combination of the SoC-e HSR-PRP switch (HPS) and the Managed Ethernet Switch (MES) IP core with redundant Ethernet switching capabilities.The MES module is a non-blocking cross-switching matrix that allows continuous transmission between all ports. It implements a store-and-forward switching method to fully satisfy the Ethernet standard policy of verifying the integrity of each frame before forwarding it. On the other hand, the HPS module introduces HSR and PRP redundancy in the required ports. Thus, the combination of MES and HPS provides the highest performance and maximum compatibility with the standard.
The following Xilinx FPGA families can support MRS:
connector
- Full-duplex 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet interface
- Half-duplex 10/100 Mbps Ethernet interface
- Full-duplex 10 Gbps Ethernet interface (under development)
- Configurable 3 to 16 Ethernet ports
- MII/GMII/RGMII/SGMII/QSGMII Physical Layer Equipment (PHY) Interface
- Each port supports different data rates
- Copper and fiber media interfaces: 10/100/1000Base-T, 100Base-FX, 1000Base-X
Time Synchronization
- IEEE 1588v2 stateless transparent clock function (P2P-Layer 2/E2E-Layer 2)
Redundancy Agreement
- RSTP (requires software stack)
Hardware Support for RSTP
Reference RSTP stack for Linux included with the IP core.
Provides Posix-compatible RSTP stacks - MRP (no software stack)
Ring Manager (MRM)
Ring Client (MRC) - DLR (no software stack)
Beacon based nodes
Supervisor Node - HSR (no software stack)
Version 3.0 (latest) - PRP (no software stack)
Version 3.0 (latest)
Supports multiple HSR modes
Supported PRP modes: Repeat Discard, Repeat Accept
Reference Design Supported Boards
- SoC-e SMARTzynq brick
exchange
- Dynamic MAC table with automatic MAC address learning and aging (up to 2048 entries)
- Static MAC table (up to 2048 entries)
- Giant Frame Management
- Ethernet-based switching
- Entrance Port Mirror
- Broadcast/Multicast Storm Protection
- Rate limiting per port (broadcast, multicast and unicast traffic)
configure
- MDIO, UART, AXI4-Lite or CoE (Configuration over Ethernet) management interface
- Configuration over Ethernet (COE): Full access to internal registers via the same Ethernet link to the CPU
- Drivers are provided with the purchase of IP cores
Distribution management
- Multicast Frame Filtering
- Switching Port Mask: User-defined frame forwarding to specific ports.
- Port-based VLAN support
- Quality of Service (QoS) Prioritization (PCP-802.1p, DSCP TOS, Ethertype)
- IEEE 802.1X EAPOL hardware processing
- DSA (Distributed Switching Architecture) Tagging: Ideally, the use of DSA would be ideal if the Ethernet switch supports "switch tagging", a hardware feature that allows the switch to insert a specific tag for each Ethernet frame received from a specific port to aid in management interface determination:
Which port is the frame from?
What is the reason for forwarding this frame?
How to send CPU-initiated traffic to a specific port
Keeping up with the times and innovating - Explore more potentials of TSN with Hongke
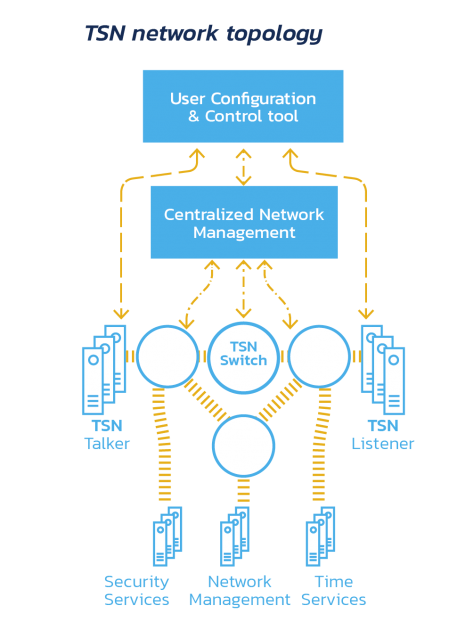
Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a new generation of network technology based on the evolution of the standard Ethernet architecture. It takes traditional Ethernet as the network foundation and provides a data link layer protocol specification for deterministic data transmission capability through mechanisms such as clock synchronization, data scheduling, and network configuration. Compared with traditional Ethernet, TSN can provide microsecond-level deterministic services, reduce the complexity of the entire communication network, and realize the convergence of information technology (IT) and operation technology (OT). With its precise clock synchronization, deterministic traffic scheduling, and intelligent and open operation and maintenance management framework, TSN can ensure the high-quality transmission of multiple business traffic in a common network, and it has both performance and cost advantages, and it is the development trend of the future network. This is the future trend of network development.
Currently, TSN technology has a high level of discussion in the automotive, industrial, rail transportation, and aerospace fields. As a non-vendor-bound real-time communication protocol, we believe that TSN technology has a good application prospect.
Welcome to contact us to explore and learn the integration of TSN technology with various industries, and actively promote more applications on the ground to jointly build a new world of intelligent interconnection.

