【虹科方案】虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案 – 整合 AI 翻譯與遠程會診,推動跨國醫療合作
虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案整合醫療級 AR 智慧眼鏡、AI 即時翻譯與遠程會診技術,支援跨語言醫療溝通、臨床教學與國際醫療合作,推動智慧醫療流程數位化升級。
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
As the earliest in-vehicle and industrial communication bus standard, traditional CAN (including CAN CC and CAN FD) has laid the foundation of embedded communication in decades of development, but its technical bottleneck has been gradually highlighted with the explosion of the demand for intelligence and networking. In the face of the limitations of traditional CAN, the industry is in urgent need of a new generation of CAN technology that is not only compatible with the existing ecosystem, but also breaks through the performance bottleneck.
CAN XL It is against this backdrop that the CAN standardization organization CiA (CAN in Automation) was developed, with a clear core objective: to retain the advantages of traditional CAN in terms of "simplicity, reliability, and low cost," while at the same time breaking through the "speed" and "capacity" ceilings.

Data length limitation: CAN CC only supports a maximum of 8-bit bytes of data, and even if CAN FD is extended to 64-bit bytes, it will still not be able to meet the high capacity requirements of modern scenarios.
For example, single-frame point cloud data from a laser radar, image segments from a high-definition camera, and full-volume status parameters from industrial equipment require hundreds to thousands of bytes of transmission capacity, which is difficult to be carried by traditional CAN.
Rate ceilings are obvious: The maximum rate of CAN CC is 1Mbps, and the maximum rate of CAN FD data stage is 8Mbps, which is not compatible with high bandwidth scenarios. (All of our PCAN devices support CAN FD baud rate up to 12Mbps)
In the case of intelligent driving in automobiles, for example, real-time data interactions between domain controllers and sensors (e.g., high-frequency detection results from millimeter-wave radar) require higher transmission efficiency, and conventional rates can lead to data delays or loss.
CAN XL TechnologyThe core competence of the company is essentially "thePrecision breakthrough on the basis of compatibility" - Both reservationsLegacy CAN BusThe advantages of low cost and high reliability are realized through thePhysical Layer OptimizationandProtocol Layer ReorganizationRealizationperformancesandfunctionalityIt is a complete upgrade of the The technology is designed to work fromPhysical LayerandAgreement LayerTwo dimensions are analyzed in depth.

CAN XL follow directly CAN FD The "infrastructure" of the organization:Dual-wire (CAN_High / CAN_Low),120Ω Terminal Resistance,Linear TopologyThis means that there is no need to dismantle the wiring in the vehicle. This means that car manufacturers don't need to remove the wiring in the car, and factories don't need to change the wiring in the shop, they just need to replace the support system. CAN XL The upgrade can be accomplished with a single device, dramatically reducing the number ofRelocation CostsThe
TransceiverIt's "Speed Up Key"There are a variety of types available. CAN XLThe
CAN SIC XL Transceiverrely on CiA610-3 StandardinData StageMaximum 20Mbit/sand is equipped with SIC Modeand FAST mode::
SIC Mode: their behavior is similar to that of CAN SIC TransceiverAdoptionVisible / Invisible SignalThe
FAST mode: realizing higher bit rates.TX Nodeadoptpush-pull (0/1) mode(math.) genusRX NodeAdjustment threshold, but this modeError frames are not supportedThe
existArbitration StageThe system utilizes CAN SIC Transceiver Concepts (SIC Mode); inData Stagethen select push-pull transceiver Concepts (FAST modeThe first is the "Crowd".) Through thisMode Switching(math.) genusCAN XL Realize up to 20Mbit/s of the bitrate.
exist CAN XL Agreement(used form a nominal expression) ADS (Arbitration to Data Sequence) phaseThe transceiver will receive the data from the SIC ModeSwitch to FAST modeThe mode switching is done by the CAN XL Protocol ControllerThrough TxD PinCarry out control.
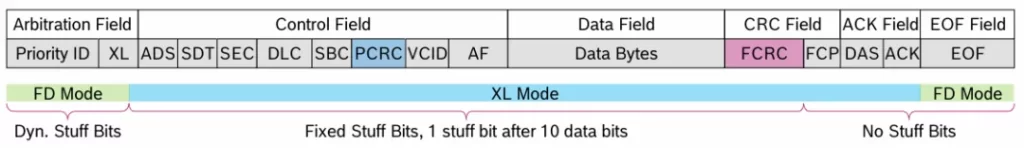
CAN XL rightFrame StructureIt has been reorganized to include a number of newSmart Function Bits", which can both carry 2048 bytesThe data can be accurately matched with the data of the CAN,EthernetDifferent scenes.
PID (Priority ID): 11-bit, used only forBus ArbitrationandPriority JudgmentThe address function is no longer committed, and the address will be changed by the successor. Paragraph AFDone.
Section XL: Includes rrs, ide, fdf, xlf Four bits.
RRS: Remote requests no longer support remote frames.
IDE: Only 11-digit IDs are supported, fixed to obvious.
FDF/XLF: Indicates that the frame is CAN FD framemaybe CAN XL FrameThe
ADS (Arbitration Data Sequence)The following are some examples of the types of data that can be used in the following areas: 4 digits, labeling fromArbitration Stage(≤1Mbit/s) switched toData Stage(up to 20Mbit/s).
SDT (SDU Type): 8-bit, embedded in the definition data fieldAgreement Type(Ethernet-like) EtherTypeThe program supports 256 types.
SEC: 1 bit, indicates whether theEncrypted DataThe
DLC (Data Length Code): 11-bit, defined data length, support for 1-2048 bytesThe
SBC (Stuff Bit Count): 3 digits, records SOF (Start of Frame) and Arbitration FieldsThe number of bit fills helps the receiver to process them correctly to ensure transmission accuracy.
PCRC (Preface CRC): 13 bits for verification of the first half of the arbitration and control fields, realizing the "Early Error DetectionThe "Error Frame Processing" is a quick termination of the error frame processing.
VCID (Virtual CAN Network ID): 8-bit, Ethernet-like VLAN IDThe physical bus can be divided into 256 virtual networksThe new system is designed to increase isolation and flexibility (e.g., body compartmentalization).
AF (Acceptance Field): 32-bit forAddress LabelingThe meaning of the term is defined by SDT decision and is included in the controller's 64-bit Hardware FilterCenter.
Data Bytes (1-2048 bytes): Carries actual data, can transmit signals directly, packaging CAN FD framemaybeEthernet frames (including IPv6, etc.)The agreement is to reduce agreed expenses.
FCRC (Frame CRC)The 32-bit calibration of the entire frame (from arbitration to data fields) ensures accuracy at high transmission speeds.
FCP (Format Check Pattern): 4-bit for Receive SideBitstream Alignmentto avoid errors caused by synchronization deviations.
DAS (Data Arbitration Sequence)The following are some examples of the types of data that can be used in the following areas: 4 digits, labeling fromData Stagecut backArbitration StageThe bitrate switching.
ACK (Positive Acknowledgement): 1-bit, same as CAN FD The mechanism is consistent, and the receiver confirms the successful reception of the frame by means of a dominant bit.
EOF (End of Frame)The following 11 implicit bits identify the end of the frame, and are associated with theTraditional CANCompatible.
CAN XL compatibleEthernet Layer ProtocolandCAN Communicationfunded by SDT and AF fields are co-implemented.
SDT The length is 8 bits and can be defined theoretically. 256 Service Data Unit (SDU) typesThe
In practice, the values are standardized and extended by the relevant standards. CurrentlyCiA611-1 SpecificationThe first edition defined 5 SDU types::
Content Based Addressing
Node Addressing
Classical & FD Frame Tunneling
IEEE 802.3 (Eth) Tunneling
IEEE 802.3 (Eth) mapped Tunneling
We will continue to expand the number of categories and further strengthen the CAN XL cross-protocol compatibility.
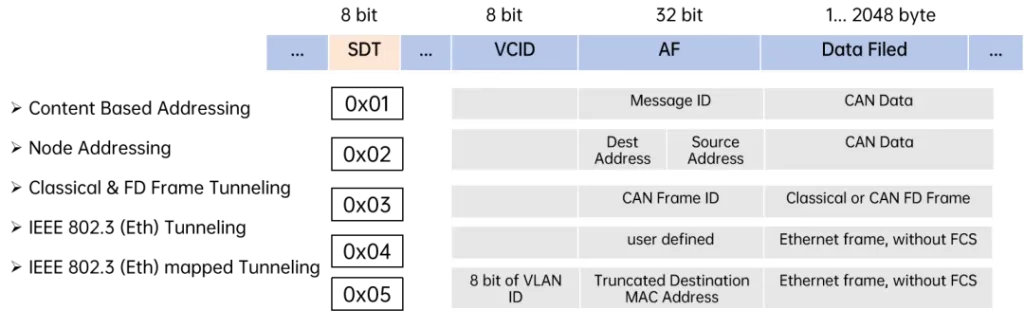
When SDT Value = 0x01 (Content Based Addressing) Time.AF is interpreted as Message IDForContent-based addressingThe
When SDT Value = 0x02 (Node Addressing) Time.AF sustain Target Address (Dest. Address) and Source Address (Address Source)RealizationNode-based addressingThe
When SDT Value = 0x03 (CAN CC & FD Frame Transmission, Classical & FD Frame Tunneling) Time.AF incorporate CAN Frame ID (11- or 29-digit ID)For use in the transmission of CAN CC maybe CAN FD frameThe process will be recognized and processed at the same time.
When SDT value = 0x04 (IEEE 802.3 (Eth) Transmission) maybe 0x05 (IEEE 802.3 (Eth) mapping transmission) Time.AF fieldFor carrying andEthernet address information(e.g.User-defined,Intercepted destination MAC addressetc.) in order to CAN XL NetworkRealizationEthernet Frame TransferThe

Stronger.TechnologyIf there is a shortage of goodartifactIt is also difficult to really get off the ground. Many users have just come into contact with CAN XL When you do not have any interfacing equipment, you often wonder, "What should I do if I don't have any interfacing equipment? What software should I use to analyze the frame data?" --What software can I use to analyze the frame data? Rainbow PCAN XL KitIt's the perfect solution to these entry points, and it's all in one package.Hardware Connection + Software Analysis".
Rainbow PCAN XL KitContains:
USB to CAN XL Interface
Professional CAN Analysis Software PCAN-Explorer 7 Sneak Peek Version
PCAN-Basic Programming Interface
To get started CAN XL Standardusers to provide the requiredFull ToolchainThe
Considering CAN XL Newsletterand CAN CC Same, at least two are needed.Bus NodeHONGKEI offers the following features in the kit model design Single interface (1 × PCAN-USB XL) and Dual Interface (2 × PCAN-USB XL) Two options. Even if there is no suitable CAN XL Docking DeviceYou can also easily go through the experience.New Generation StandardsThe first step in the process.
finish chattingTechnologyandartifactHowever, many people will still have practical questions:securityHow is it safeguarded?TestingTo do what?Industry ExpertsHow do you see the future trend? -- HOSCOI'm going to take you through them one by one. CAN XL Frequently Asked QuestionsThe
Q1: What are the security enhancements of CAN XL over traditional CAN?
A1: CAN XL Not available per seencryptedmaybeAccreditation MechanismandEthernetSimilar, security depends onSupervisory AgreementmaybeHardware Security Modules(e.g.cryptographic engine). Currently CANsec (CAN security standard) It's in development. It's expected. End of 2025is completed and will be used to define theData EncryptionandIdentity verification mechanismThe
Q2: What is the limitation of total wire length and wiring in fast mode?
A2: No fixed limit, depends onTopologyandElectromagnetic Environment. For example. 1Mbps Arbitration StageThe total line length is usually about 1.5 meters. 40 metersIf the bit rate is lowered, the bus length can be extended.Branch LengthNeed to be based on the actualSignal QualityAdjustments will be made. TheirLayout constraintsand CAN FD Basic consistency, existing buses can be reused, only need to change support CAN XL (used form a nominal expression) ECU It is possible to increase the rate.
Q3:How to improve the scalability and security of CAN XL's VCID (Virtual Local Area Network)? What are the difficulties?
A3: Through 8-bit VCID The virtual bus can be divided to isolate different domains (e.g.body area,Dynamic Domain) and filtering at the hardware level.Unauthorized VCID TrafficPreventing ECU Attacked by Unauthorized Messages. The challenge isSoftware & HardwareAll need support Virtual ID (used form a nominal expression)Filtering and RoutingThe
Q4: What are the advantages of CAN XL over Ethernet (e.g. 10BASE-T1S)?
A4: CAN XL The advantage of this is that it can beFlexible Bit Rate Adjustment(adapts to different network environments), no need toCenter Node(to avoid single point of failure). AndEthernet(e.g. 10BASE-T1S) requires a fixed rate and relies on the center node.
Q5:Are there any commercial MCUs / toolchains that support CAN XL?
A5: HONGKE PCAN-USB XL support sth. Windows / Linux Driver.;HONGKEI PCAN-Explorer 7 resolvable CAN XL Frameand provideOpen API For third party development. Welcome to contact Hongke StaffLearn the details.
Q6:What tests are required for module level verification? Is there any mandatory certification?
A6: Underlying protocol conformance testingcomply with ISO Standard.;High-Level Security / Consistency Certification(e.g. CANsec(still under development and not available at this time)Mandatory RequirementsThe

虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案整合醫療級 AR 智慧眼鏡、AI 即時翻譯與遠程會診技術,支援跨語言醫療溝通、臨床教學與國際醫療合作,推動智慧醫療流程數位化升級。

虹科 PCAN 卡應用於隧道挖掘設備電控系統,支援 CAN / CANopen / J1939 通訊,協助工程設備實現穩定資料傳輸、精準控制與高可靠性運作,適用於鑿岩台車與隧道施工設備。

KnowBe4 為企業應對香港《關鍵基礎設施保護條例》提供了化繁為簡的解決方案。面對第 24 條與第 25 條的嚴格挑戰,它將難以量化的「人為風險」轉變為可追蹤的實戰數據,不僅彌補了傳統評估的盲點,更為年度審核提供了證明控制措施「有效運作」的鐵證。透過自動化報告與持續演練,企業能在大幅降低安全風險的同時,輕鬆滿足監管要求,實現從「被動合規」到「主動防禦」的關鍵轉型。