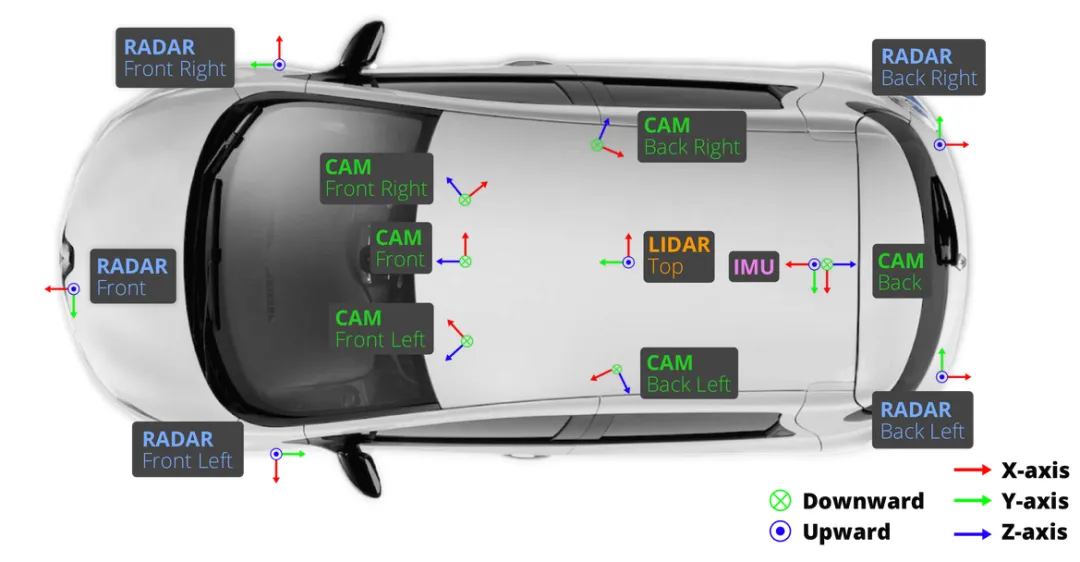
【虹科方案】 SimData 高保真虛擬數據集 – 基於 aiSim 的自動駕駛多傳感器感知數據方案
SimData 為基於 aiSim 仿真平台生成的高保真虛擬感知數據集,支援 Camera、LiDAR、Radar、IMU 多傳感器同步數據,結構完全對齊 nuScenes,可直接使用 nuscenes-devkit 進行解析與模型訓練。
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) is gradually penetrating into every industry and everywhere, how can embedded smart devices achieve efficient and reliable collaboration between massive data and real-time demands? The answer may not come from a new and disruptive technology, but from a classic, mature, and still very much alive cornerstone....CAN busThe
Here, we share CiA's authoritative viewpoints and bring you an in-depth discussion on how CAN, with its core features of "high reliability, real-time performance, and distributed architecture," can reshape its own positioning in the rising tide of embedded AI.
Have you noticed that AI is gradually sinking from the "cloud" and quietly embedding itself into all kinds of terminal devices around you? This trend is the so-called "embedded AI", which allows devices to have the ability to sense, reason, judge and act autonomously locally.
However, a new question arises: how can these "small intelligences" scattered at the periphery be stably, securely, and with low latency linked together to form a reliable collaborative system?
The answer, perhaps, lies in the widely validated and continuously evolving communications technology - theCAN busThe
The latest article of CiA (CAN in Automation), an international authority, will reveal how the technology combination of "CAN + AI" will lay a stronger foundation for future intelligent systems. It's about a more efficient, autonomous and intelligent embedded world, and this future is approaching at an alarming speed.

Google AI defines embedded AI as "the deep fusion of artificial intelligence with physical devices and systems". Through this convergence, devices no longer have to rely on cloud connectivity and can process data, analyze intelligence, make decisions and even execute actions locally.
To achieve these capabilities, "lean" AI models need to be run on highly efficient hardware to improve computational efficiency, accuracy and real-time response. Typical applications include autonomous robots, smart sensors, medical devices, and smart manufacturing.
Embedded AI is seen as the next stage in the evolution of embedded control networks. Back in the early days of AI, AI relied on large clusters of remote computers with high energy consumption and was fed by sensors in embedded networks, which were computed in the cloud and sent back to front-end actuators for control.
However, with the increasing demand for real-time performance, cloud-based architectures are no longer sufficient for latency-sensitive embedded control scenarios that must respond quickly. This has led the industry to deploy Edge AI ControllerThe AI calculations are performed closer to the scene to minimize latency.
The next step for embedded control networks is to allow AI to be decentralized to the AI-based sensors and AI-based actuators themselves, allowing them to choose whether or not to communicate with local edge AI controllers on demand, making the entire system more flexible and autonomous.
In the development of new technologies, centralized architectures are often the starting point; as they mature, they usually move towards decentralized architectures. The benefits of decentralization are clear: trained, pre-processed data is smaller, and true real-time communication is possible even on low-bandwidth networks.
This is crucial for all autonomous equipment, such as AGVs, AMRs, drones, self-driving agricultural machinery, forestry equipment, construction machinery, earthmoving equipment, etc.
Looking back at historical applications, we can see that these autonomous systems have generally adopted a distributed network architecture based on CAN buses; this is also true in areas such as medical equipment and laboratory equipment. In addition, the decentralized architecture brings an extra security advantage: Embedded AI networks do not have to rely on remote interfaces, so they are more immune to external network attacks, which significantly improves system security.
The first batch of embedded AI devices to hit the ground are expected to focus on two areas:
Multi-sensor fusion equipment for navigational purposes-Output intelligent data processed by AI algorithms
Condition Monitoring Equipment-Predictive Analytics and Health Diagnostics with Embedded AI
In terms of actuators, intelligent power drives that support self-configuring and self-optimizing will become typical applications for embedded AI. In addition, predictive maintenance and AI status monitoring of electrical equipment are also the focus of various industries.
While using an embedded real-time AI host controller is an option, integrating the AI software directly into the actuator effectively lowers the system design threshold and saves engineers significant development and integration costs.
There is reason to believe that chipmakers will soon introduce more AI-friendly hardware with lower power consumption and more reasonable costs, making it easier to deploy embedded AI in battery-powered devices.
In the author's opinion:The CAN bus-based network architecture is optimal for connecting AI sensors, AI actuators and master controllers in series.
The high stability, high reliability and excellent scalability of CAN are the most essential core features of an embedded AI real-time control system.
The first CANopen protocol designed specifically for embedded AI devices is the first CANopen protocol for item inspection devices. CiA 462The
Rather than relying on specific sensing technologies (e.g., camera, radar, ultrasound, etc.), it explicitly defines the data format that can be mapped to PDO (Process Data Object) reports, allowing multi-sensor fusion devices to output intelligent data processed by AI.
In addition, other CiA protocols will be expanded with the development of embedded AI, especially in the areas of status monitoring and device health parameters, which will see more comprehensive upgrades.

Embedded AI is accelerating to the edge, and a stable, reliable, and highly real-time communications architecture is a critical foundation for it to take hold. As this paper reveals, theCAN and CANopen are becoming the ideal "neural network" for embedded AI.The next generation of highly autonomous smart devices will be supported by the next generation of highly autonomous smart devices.
In the face of this wave, Avision is committed to delivering products that range from the classic to the cutting edge (including the latest 👉). Rainbow PCAN XL KitWe are looking forward to working with our industry partners to usher in the era of "Embedded AI × Real-time Control Network" convergence. We look forward to working with our industry partners to embrace the new era of "Embedded AI × Real-time Control Network" convergence.

SimData 為基於 aiSim 仿真平台生成的高保真虛擬感知數據集,支援 Camera、LiDAR、Radar、IMU 多傳感器同步數據,結構完全對齊 nuScenes,可直接使用 nuscenes-devkit 進行解析與模型訓練。
虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案整合醫療級 AR 智慧眼鏡、AI 即時翻譯與遠程會診技術,支援跨語言醫療溝通、臨床教學與國際醫療合作,推動智慧醫療流程數位化升級。

虹科 PCAN 卡應用於隧道挖掘設備電控系統,支援 CAN / CANopen / J1939 通訊,協助工程設備實現穩定資料傳輸、精準控制與高可靠性運作,適用於鑿岩台車與隧道施工設備。