【虹科方案】虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案 – 整合 AI 翻譯與遠程會診,推動跨國醫療合作
虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案整合醫療級 AR 智慧眼鏡、AI 即時翻譯與遠程會診技術,支援跨語言醫療溝通、臨床教學與國際醫療合作,推動智慧醫療流程數位化升級。
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
dSPACE, a world-renowned provider of simulation and verification solutions, has successfully constructed a GNSS-based Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) simulation system for driving functions. The system can be widely used in automotive scenarios such as autonomous driving, V2X, and smart cabins, and is highly flexible and versatile, making it suitable for all kinds of complex test environments.
dSPACE is a global player in the field of simulation and verification, and a pioneer in aerospace and defense innovation. Its product portfolio covers the entire development chain from conceptual design to mass production support for applications in autonomous driving, electric vehicles, motors, battery management systems, fuel cells, power electronics, charging infrastructure, and more.
dSPACE also offers a wide range of simulation models to support all stages of development, from functional development to ECU testing.

The importance of GNSS signals in autonomous driving lies in their ability to provide accurate, reliable and stable positioning information. Whether it is V2X communication or autonomous driving function verification, all core applications rely on satellite-supported positioning capabilities.
However, the availability of different GNSS systems varies greatly, and the quality of GNSS signals can be easily affected by topographical environments (e.g., urban canyons, viaducts, dense buildings). In addition, GNSS signals can be subject to unintentional interference, malicious interference, or spoofing attacks.
To ensure the robustness and reliability of the application in everyday scenarios, it is essential to rely on more powerful and stable GNSS simulators.

The whole system is mainly composed of the following parts:
In this solution, the HIL simulator can specify the 3D trajectory and related scenes, and output the position information (latitude, longitude, altitude), 3-axis velocity, 3-axis acceleration and acceleration. Attitude information such as 3-axis angular velocity can be obtained using an ASM module, and the data is transmitted in real time to the GNSS simulator, which then feeds it back to the device to be tested using RF signals.
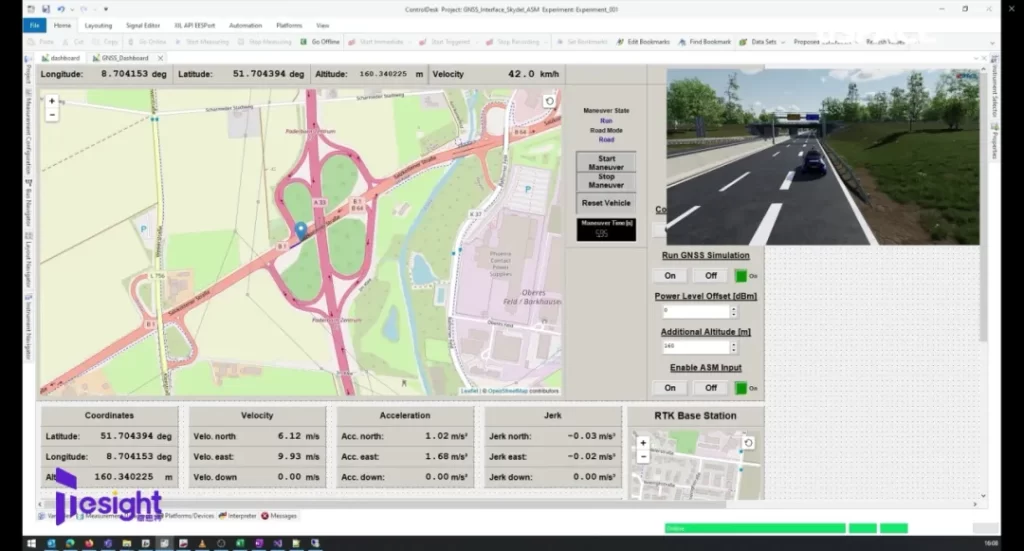
During the GNSS simulation process, you can observe the GNSS data output from the simulator and received from the device under test in real time, and you can check the positioning error and compare the performance of the simulation coordinates. By monitoring the interaction between the GNSS simulator and the DUT (Device Under Test) in real time, the performance of the positioning algorithm and GNSS modules in different environments can be more accurately evaluated.
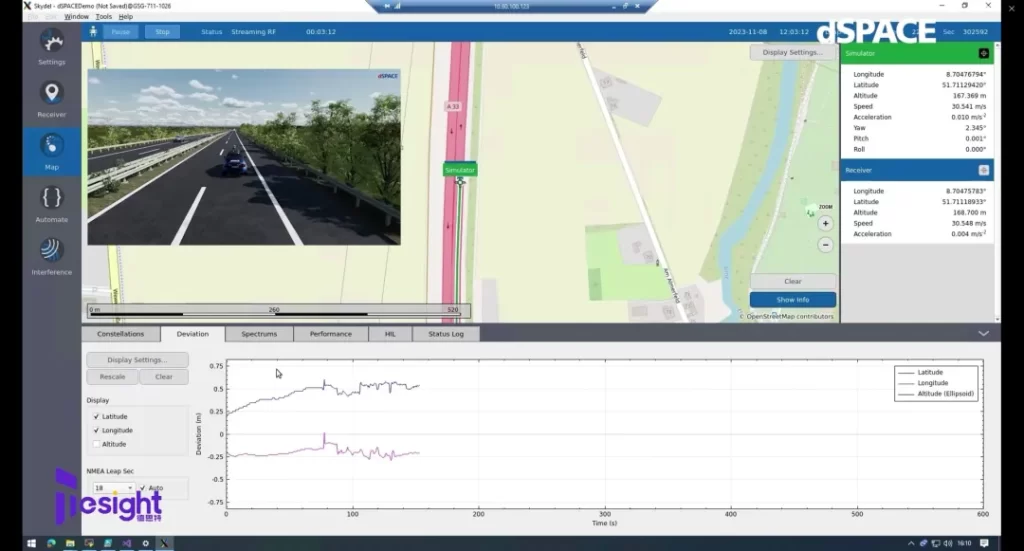
In this way, the GNSS module can be fully integrated into HIL's 3D simulation scenarios, enabling it to perform a wide range of complex environmental and operational tests in a laboratory environment. The ability to simulate a wide range of road conditions and environmental changes without the need for extensive on-road measurements dramatically improves testing efficiency, while providing more quantifiable data for performance optimization and algorithm adjustment.
The GNSS simulator enables highly accurate geolocation simulation and satellite signal generation. When the GNSS signal generator is integrated into the dSPACE ASM model, the system automatically selects the default GNSS test scene and controls the signal generator.
In a typical autonomous driving test, the starting position, date, driving route and driving maneuvers can be parameterized in the ASM model, and various GNSS constellations (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou, etc.) and signal degradation modes can be selected. the HIL simulator continuously transmits the vehicle position data to the signal generator, which generates a simulated signal based on the scene and outputs it as a real RF signal to the GNSS device to be tested. The HIL simulator continuously transmits the vehicle position data to the signal generator, which generates a simulated signal based on the scene and outputs it to the GNSS device to be tested in the form of a real RF signal.
Through this complete process, the positioning status, error behavior and performance limits of GNSS modules in various complex scenarios can be completely reconstructed, effectively supporting the rapid verification of autonomous driving perception and positioning tests.

虹科 AR 遠程醫療解決方案整合醫療級 AR 智慧眼鏡、AI 即時翻譯與遠程會診技術,支援跨語言醫療溝通、臨床教學與國際醫療合作,推動智慧醫療流程數位化升級。

虹科 PCAN 卡應用於隧道挖掘設備電控系統,支援 CAN / CANopen / J1939 通訊,協助工程設備實現穩定資料傳輸、精準控制與高可靠性運作,適用於鑿岩台車與隧道施工設備。

KnowBe4 為企業應對香港《關鍵基礎設施保護條例》提供了化繁為簡的解決方案。面對第 24 條與第 25 條的嚴格挑戰,它將難以量化的「人為風險」轉變為可追蹤的實戰數據,不僅彌補了傳統評估的盲點,更為年度審核提供了證明控制措施「有效運作」的鐵證。透過自動化報告與持續演練,企業能在大幅降低安全風險的同時,輕鬆滿足監管要求,實現從「被動合規」到「主動防禦」的關鍵轉型。